|
What Is RAID?
As it was originally proposed, the acronym RAID stood for
Redundant Array of Inexpensive Disks. However, it has since come to be known
as Redundant Array of Independent Disks. RAID was originally described in the
paper "A Case for Redundant Arrays of Inexpensive Disks (RAID)" written by
three University of California Berkeley researchers: David Patterson, Garth
Gibson, and Randy Katz. The concept was presented at the 1988 conference of
the ACM Special Interest Group on Management of Data (SIGMOD). In the
original Berkeley paper there were five RAID levels (1-5). RAID-6 was added
later as an enhancement for RAID-5. In time other levels have
been implemented by various companies using the concepts described in
the original proposal. These include RAID-0 (striping without redundancy),
and multilevel RAID (striping across RAID arrays), and others variants.
The Levels of RAID
|
RAID 0 |
RAID 1 |
RAID
10
(also known as RAID 0/1) |
RAID 5 |
| Description |
Data striping
(no data
protection) |
Disk mirroring |
RAID 0 and RAID 1 combined |
Data striping with distributed
parity |
| Minimum # of Drives |
Two |
Two |
Four |
Three |
| Benefit |
Highest performance |
Data protection through
redundancy |
Highest performance with data
protection |
Best balance
of
cost/
performance/
data protection |
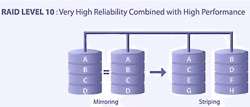
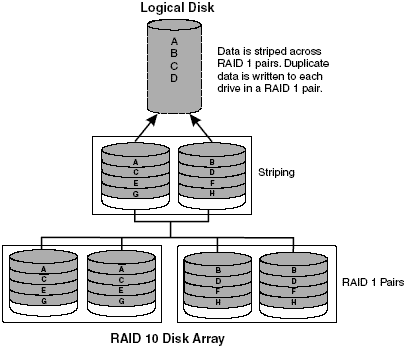
RAID 10 (Mirroring + Striping)
- RAID 10 is implemented as a striped array whose segments are RAID 1 arrays
- RAID 10 has the same fault tolerance as RAID level 1
- RAID 10 has the same overhead for fault-tolerance as mirroring alone
- High I/O rates are achieved by striping RAID 1 segments
- Under certain circumstances, RAID 10 array can sustain multiple simultaneous
drive failures
- Excellent solution for sites that would have otherwise gone with RAID 1 but
need some additional performance boost
- Very expensive / High overhead
- All drives must move in parallel to proper track lowering sustained
performance
- Very limited scalability at a very high inherent cost
- Database server requiring high
performance and fault tolerance
|